Research
Creative Source of Pioneering Work in Skin and Hair Physiology
In use almost everywhere in the world
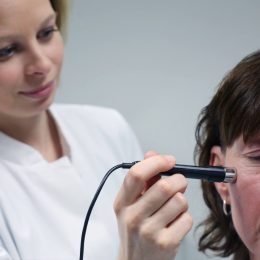



Research at Institutes Dr. Schrader has often been the starting point for development of new methods. The procedure is: first do research, then develop and test, and finally analyze.
Between the Sebumeter and ICL-S/H there lies not just 50 years of continuous, solid work but also 50 years of ideas and concepts for new skin and hair physiological measuring principles that today have matured worldwide into standard methods and instruments. Whether Corneometer or FOITS technology, Cutometer or NIR-RS, Institutes Dr. Schrader not only use cutting edge technologies but also are a constant source of new, practice-oriented methods and instruments for skin and hair physiological testing on volunteers and in laboratory.
Sebumeter / Corneometer
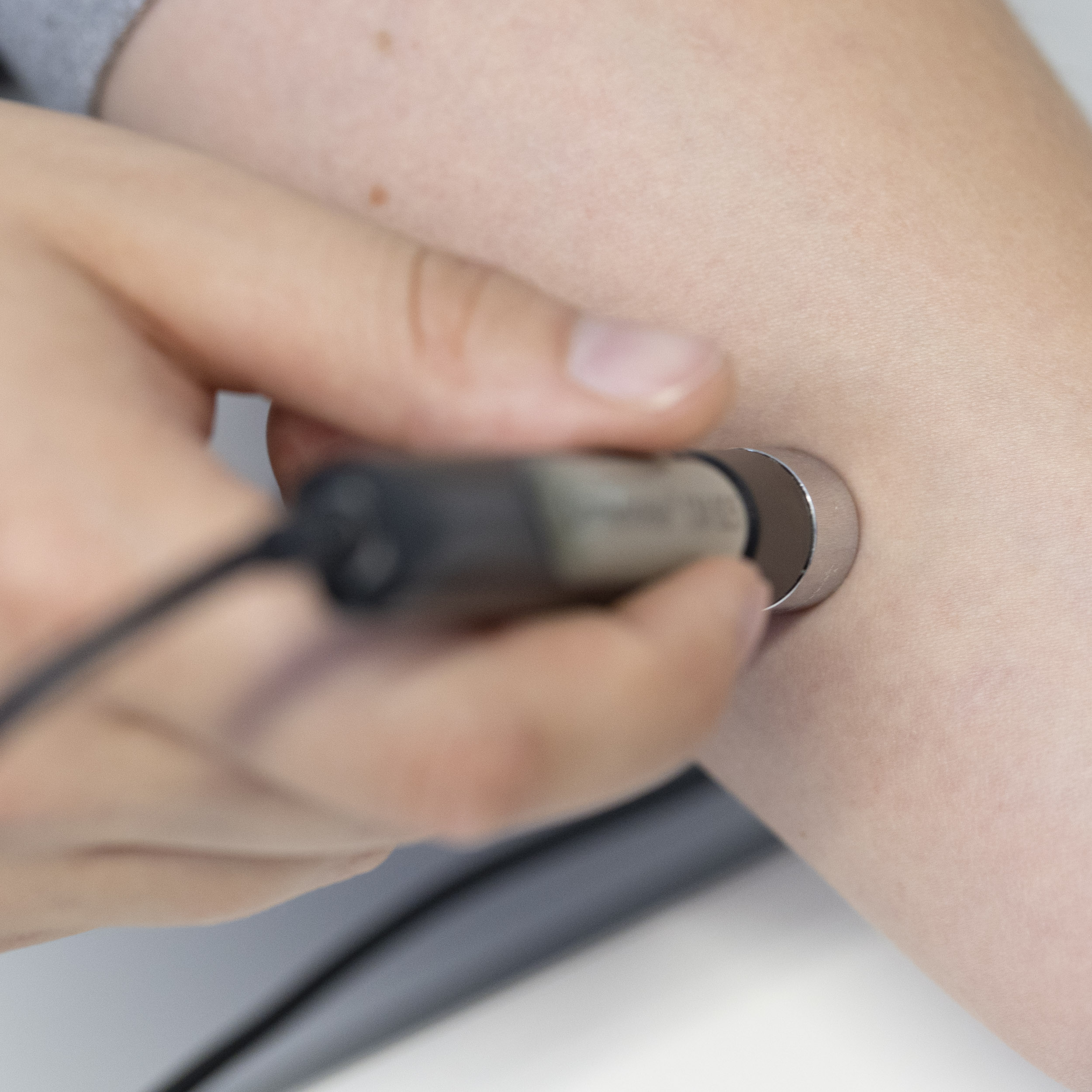
The Corneometer and Sebumeter devices developed by the Dr. Schrader institutes for determining skin moisture and oil content are used worldwide.
Practicality and scientific relevance have prevailed until today. In 1980, both devices were handed over to the Schwarzhaupt company, then to Courage & Khazaka to ensure constant technical updating and optimization.
Both devices, which are characterized by their simple and ingenious principle as a grease spot photometer and the measurement of dielectric constants, respectively, have become indispensable in cosmetic efficacy testing.
Degreasing and refatting effect – Sebumeter measurements
The protective barrier of the skin is a thin lipid film consisting of sebaceous gland lipids and water. The content of surface lipids, as well as the number of sebaceous glands, strongly depends on the skin region and ranges between 50 µg/cm² and 500 µg/cm². In the case of sebum overproduction, the skin appears greasy, which is cosmetically undesirable.
The determination of the sebum content of the skin is carried out with the Sebumeter® developed in our company. Optionally or in combination, the Sebutape® method is used.
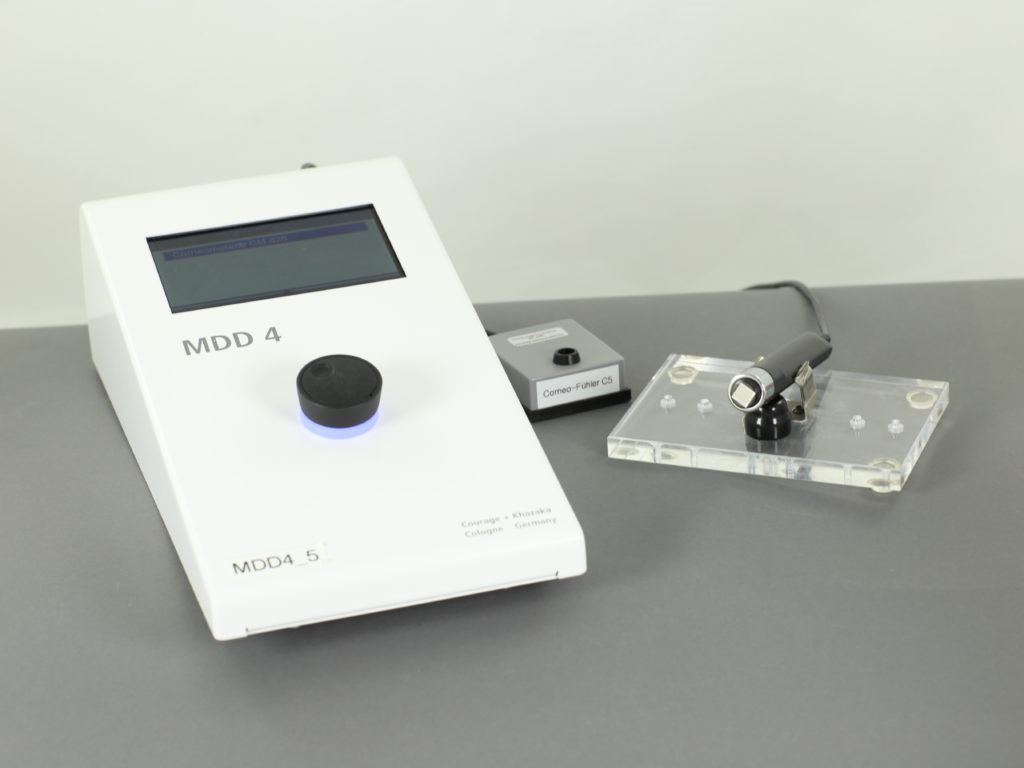

Feuchtigkeit der Haut – Corneometer Messungen
Ausreichende Feuchtigkeit ist Grundvoraussetzung für eine gepflegte und geschmeidige Haut. Daher ist die Erfassung der Hautfeuchtigkeit ein wesentlicher Bestandteil der Prüfung von kosmetischen Pflegeprodukten. Ebenso aussagekräftig ist der Nachweis der nicht austrocknenden Wirkung von Reinigungsprodukten wie Handseifen oder Duschgelen. Alle Hautfeuchtigkeitsmessungen erfolgen mit dem im unserem Haus entwickelten Corneometer.
FOITS - a Classic Device in Modern Efficacy Testing
FOITS is the abbreviation for Fast Optical in vivo Topometry of Human Skin and stands for a non-contact method of three-dimensional wrinkle analysis.
Initial studies on the topic of non-contact surface analysis of the skin were begun in 1995. After a successful validation phase, the new FOITS technique could be presented in 1997 at the Conference of the International Society for Skin Imaging in Vienna. The first publication followed at the beginning of 1998. Numerous technological advancements such as improved camera resolution, use of blue LED illumination systems or laser-aided and computer-optimized overlay procedures have made it possible in past years to achieve an efficient and easy to operate system. However, because scientific interest in the mechanisms of wrinkle evaluation has always been extremely high, technological advancements led to an instrument on a high scientific level – always in the context of cosmetic practice. Since its beginnings in 1995, Fast Optical in vivo Topometry of Human Skin (FOITS) has established itself globally and today over 40 systems are in use.
In those almost 25 years of use, new parameters for efficacy evaluation could be introduced thanks to the detailed surface analysis of the FOITS method. For example, the FDD parameter (Frequency Distribution of Depth) allows a depth-related efficacy analysis based on a statistical method. The Area-Analysis possible with the FOITS technique where different areas and depths of wrinkles are considered in the wrinkle analysis is another example of how new findings on the history of wrinkle formation as well as a detailed product-related efficacy analysis can be obtained. Newer studies with our joint venture partner institute in Beijing have revealed interesting differences in the topometry of Asian and Caucasian skin. Thus FOITS in a very short time has already become a classic in modern efficacy testing that finds worldwide use and has provided the basis for much information on wrinkle reduction but also its validation by independent organizations.
And the future is already being evaluated at Institutes Dr. Schrader. FOITS-2 has advanced the FOITS technology to a “2-Shot-One-Face-Technique” (2-SOFT) of all important test areas. Test areas such as the whole face, which are recorded in a single stereo photo, allow a parallel differentiated analysis of different wrinkle regions and are available for routine use.
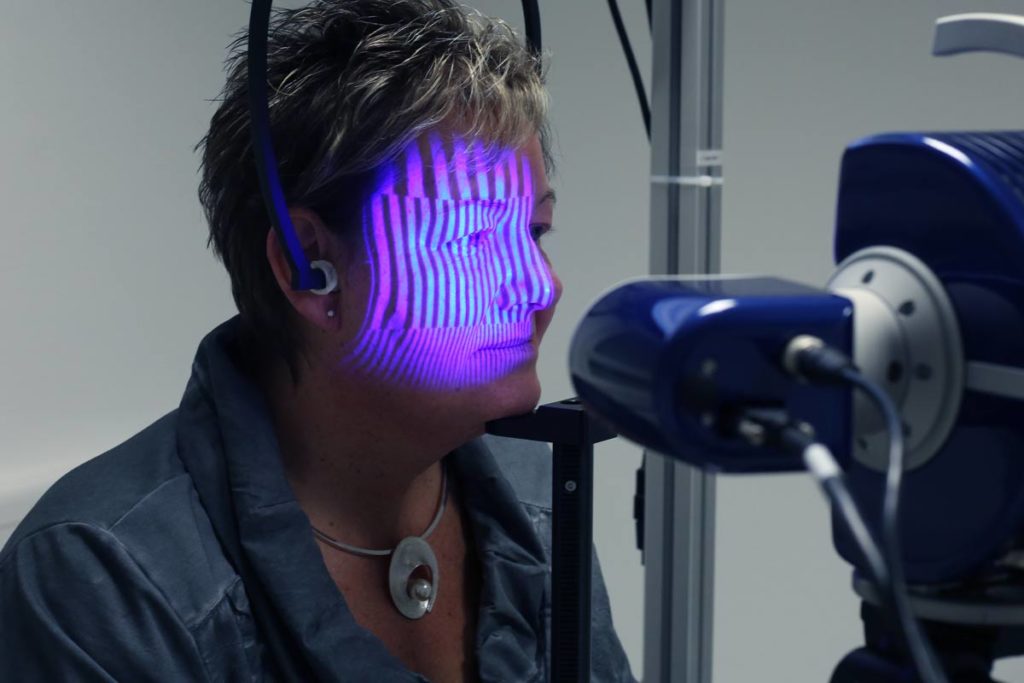

Near Infrared-Remission Spectroscopy
The highest honour went to Institutes Dr. Schrader in Orlando, Florida. The Schrader Team received the Applied Research Award 2004 at the scientific congress of the IFSCC International Federation of Societies of Cosmetic Chemists in Orlando, Florida.
NIR-RS is an optical spectral analysis in which the viewing angle is shifted from the visible spectral range to the near infrared range to allow identification of any physiological skin reactions, even those hidden by the products that induce them such as a permanent hair color. This is a technology that the IFSCC Committee valued so highly that it honoured it in 2004 with the Applied Research Award.
Near Infrared-Remission Spectroscopy
The highest honour went to Institutes Dr. Schrader in Orlando, Florida. The Schrader Team received the Applied Research Award 2004 at the scientific congress of the IFSCC International Federation of Societies of Cosmetic Chemists in Orlando, Florida.
NIR-RS is an optical spectral analysis in which the viewing angle is shifted from the visible spectral range to the near infrared range to allow identification of any physiological skin reactions, even those hidden by the products that induce them such as a permanent hair color. This is a technology that the IFSCC Committee valued so highly that it honoured it in 2004 with the Applied Research Award.

NIR-RS
Near Infrared-Remission Spectroscopy
NIR-RS is an optical spectral analysis in which the viewing angle is shifted from the visible spectral range to the near infrared range to allow identification of any physiological skin reactions, even those hidden by the products that induce them such as a permanent hair color. This is a technology that the IFSCC Committee valued so highly that it honoured it in 2004 with the Applied Research Award.
Chemilumineszenz - Proof of Antioxidant Efficacy / ICL-S/H
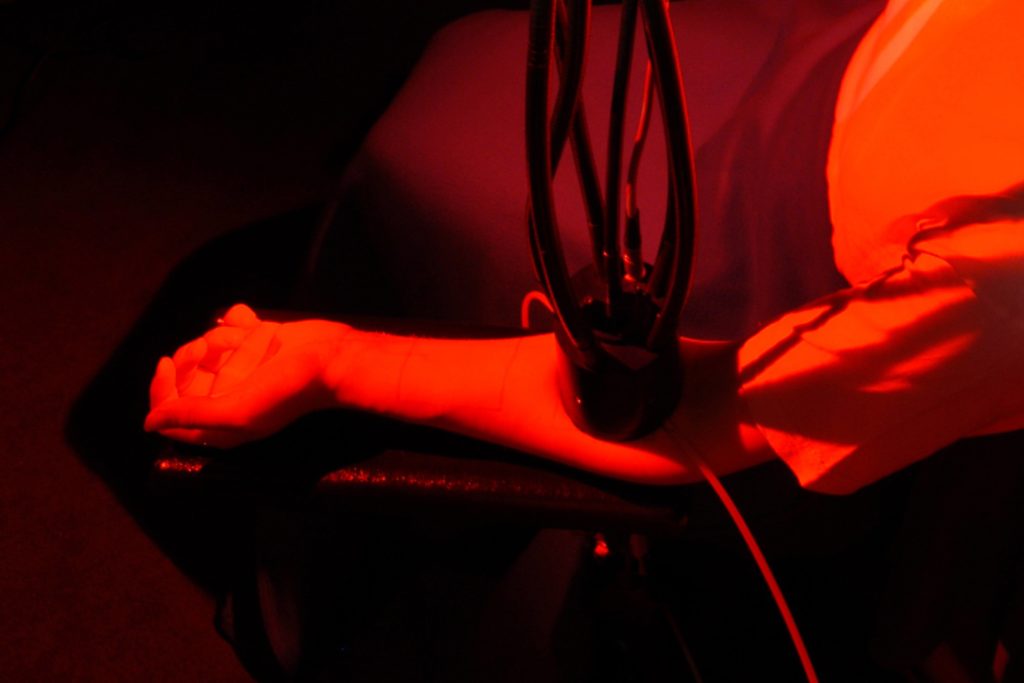

Induced chemiluminescence of skin and hair (ICL-S/H) is one of the few methods available to demonstrate in vivo an oxidative protection potential.
The chemiluminescence detection system was developed as part of a research project in collaboration with m.u.t. GmbH (Wedel, Germany) in the late 1990s. Conceived as an in vivo single photon counting system, the result was a technology that quantifies oxidative stress in the skin and hair by means of a Peltier-cooled photomultiplier.
Through spatial separation of the detection unit and control unit with sun simulator a non-invasive technique could be developed that detects photons emitted by the skin or hair less than 100 ms after stress termination and so makes it possible to obtain directly a cosmetic proof of efficacy of the oxidative protection potential.
The biggest challenge in terms of claim support is the non-invasive but at the same time sensitive measurement of oxidative stress on the test person.Only this in vivo approach takes into account all physiological processes active in living skin and provides efficacy data with the greatest possible relevance to the application situation. UV filters reduce radical formation and antioxidants cause faster and/or more effective radical neutralisation or detoxification. By measuring chemiluminescence (ultra-weak photon emission), as a concomitant of radical reactions in biological tissues such as the skin, the ICL-S method (Induced Chemiluminescence of Human Skin) allows the measurement of oxidative stress in real time in groups of test persons. The efficacy testing of antioxidants and UV filters can thus be carried out for raw materials during product development and for finished products after topical application (in-use situation), both on human skin and hair.
Anti-Dandruff – Objective Measurement of the Dandruff Status
An important goal of research at Institutes Dr. Schrader is to develop objective test methods that verify, for example, data obtained subjectively. The huge advantage of objective test methods over subjective data collection is of course an exact quantification of results.
As early as the 1980s, Institutes Dr. Schrader developed a method that allows image analysis and therefore quantitative visualization of the dandruff status of test subjects. With this method the dandruff on one half of the scalp is combed onto a prepared glass slide under standardized conditions. The dandruff is then measured by quantitative image analysis. Different image analysis algorithms are used to eliminate hair fibres and dust particles from the image and detect the dandruff by its greyscale value. This makes it possible to determine not only the amount of dandruff combed out but also its size. The measuring procedure has proved itself in practice over decades.
Continuous improvement and optimization of image analysis assure we are always able to offer our customers a reliable method.
Literatur
- Schrader K, Domsch A. (2005). Testing of Anti-Dandruff Effect in Cosmetology – Theory and Practice. Research, Test Methods, Analysis, Formulas. Verlag für chemische Industrie Augsburg, Vol. I, 230-233.
- Schrader K (1986). Comparative Experimental Research on Dandruff Through Quantitative Image Analysis. J Appl Cosmetol 4, 153-70.
- Schrader K (1982). Wirkung und Nebenwirkung Moderner Antischuppenpräparate. SÖFW J 108(15), 471-4.
HDRS - Hybride Diffuse Reflektionsspektroskopie
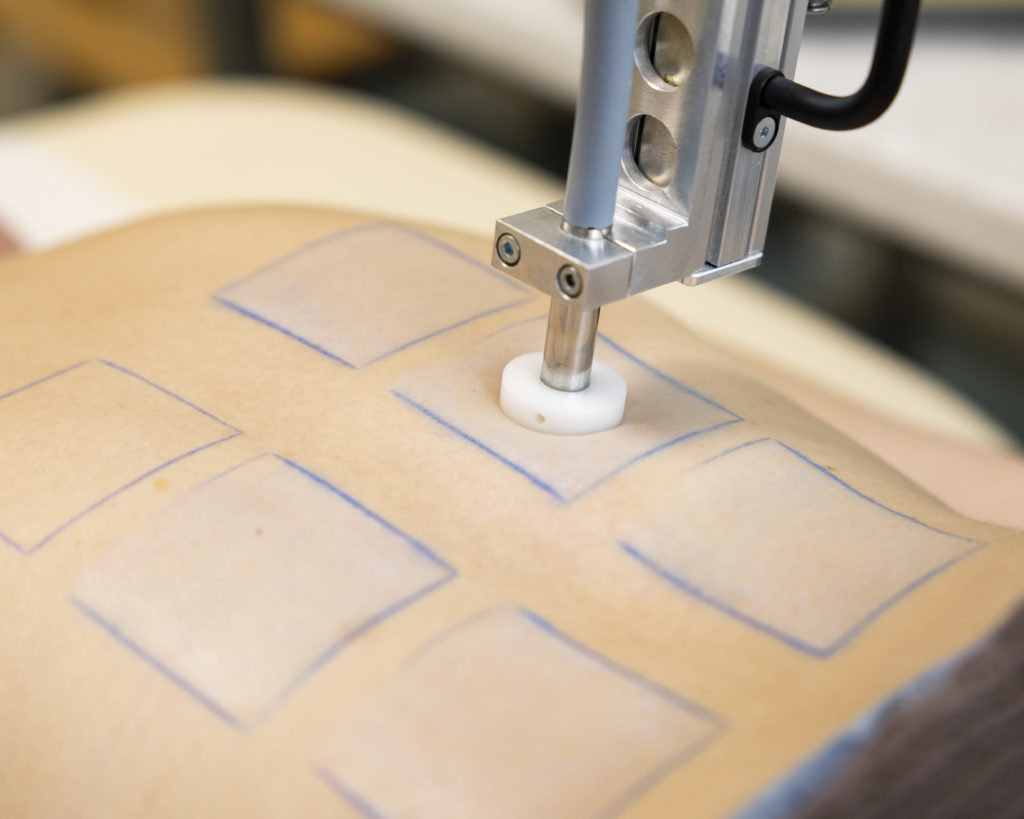


In vivo test for erythema-free SPF determination
To determine the label SPF of topically applied sunscreens in vivo, test methods such as ISO 24444, the FDA Guideline or the Australian Standard are used worldwide. The basis of all these methods is to induce an erythemal skin reaction by irradiating the skin with UV light. This is necessary to determine the minimum erythemal dose to untreated (MEDu) and product-treated skin (MEDp). Reliable in vitro methods replacing human skin with synthetic substrate carriers are still not available.
The new HDRS technique offers the possibility to still determine the sun protection factor in-vivo, but without triggering the UV radiation-induced erythemal skin reaction. It is thus an ideal solution for sun protection while addressing today’s ethical concerns.
The HDRS technique is a combination of diffuse reflectance spectroscopy (DRS) in-vivo and in-vitro transmission measurements on a roughened polymethyl methacrylate (PMMA) plate. Thus, on the one hand, the interaction of the sunscreen product with the skin is taken into account by the in-vivo measurement and, on the other hand, the UV-B absorption is measured in-vitro, since this still cannot be determined in-vivo by reflection spectroscopy. In order to establish an alternative method for in-vivo SPF determination, a large number of sunscreen products were measured using the HDRS technique and compared with the globally accepted standard ISO 24444. To validate the new method, a wide variety of different formulations as well as different SPFs (5-120) were tested.
The shown dependence of the measurement signal on the product application amount and the skin color of the test person confirms the basic correlation of the generated measurement result with the expected sun protection. Furthermore, far-reaching statistical analyses show an excellent correlation between the new, non-erythemal HDRS-SPF technique and the results obtained using the ISO 24444 method. Similarly, HDRS UVA-PF results can be correlated with UVA-PF values calculated according to ISO 24443.
By eliminating all erythema-relevant UV-B and UV-A irradiation doses during the measurement process, no skin reaction is induced in the test subjects. Consequently, MED determination is no longer necessary. For the first time, an alternative way of SPF determination is described without the ethical concerns of previous in-vivo measurement and/or the limitation of previous SPF in-vitro tests. Regardless of the type of formulation or the level of protection of the test product, an excellent correlation was found for the SPFHDRS and SPF24444 claims. This new, non-erythemal measurement method allows not only SPF values to be determined, but also UVA-PF values to be calculated from the same data, with excellent correlation to the ISO 24443 method. For the first time, a reliable alternative test method for SPF and UVA-PF determination is described that takes into account the interaction of the sunscreen with the skin.



